Introduction to Hand Saws
If you’re looking for the right cutting tool for your next project, this Hand Saw Guide will help you make the best choice. Hand saws are simple, reliable tools that every DIY enthusiast and professional should own. In this guide, you’ll learn about different types of hand saws, how to use them safely, how to maintain them, and what to look for before buying one. Whether you’re cutting wood, metal, or plastic, the right hand saw can make your work faster and more precise.
Table of Contents
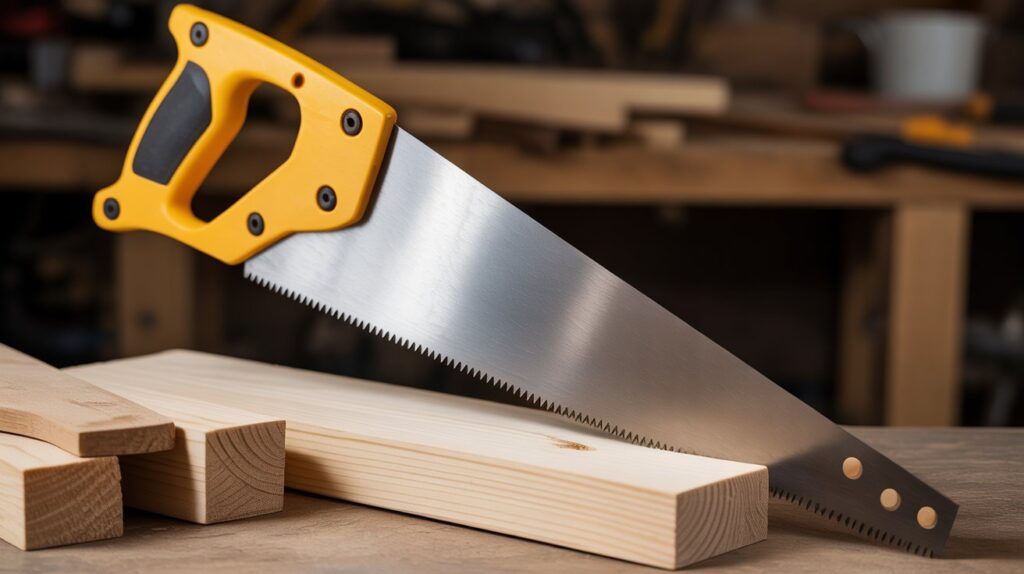

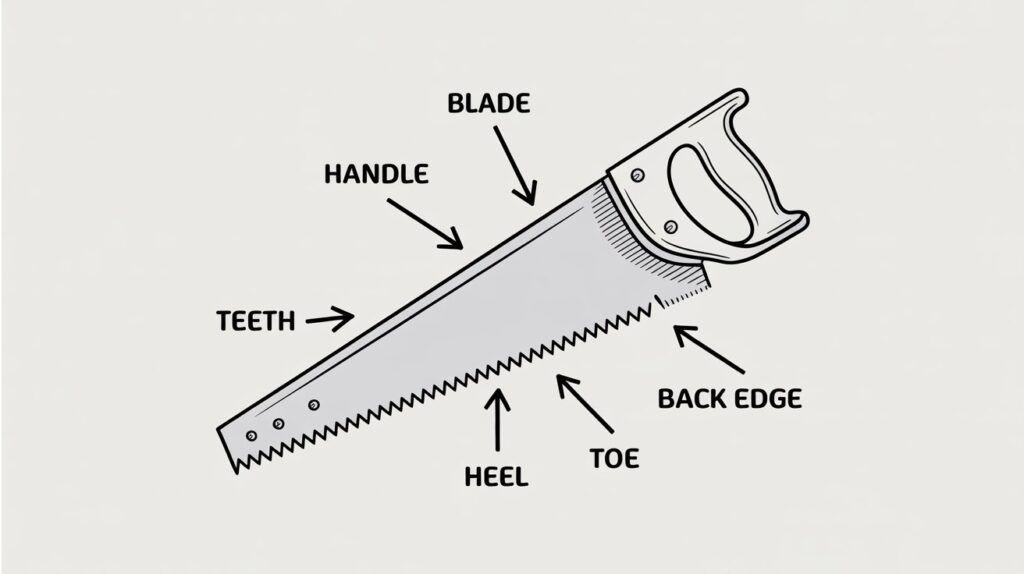
Parts of a Hand Saw
Understanding the parts of a hand saw is essential before learning how to use it effectively. Each component plays a specific role in providing precision, comfort, and control during cutting. In this section of our hand saw guide, we’ll break down the key parts and their functions in a clear and simple way.
Handle (Grip)
The handle, also known as the grip, is where you hold the saw. It’s usually made from wood, plastic, or rubber for comfort and stability. A well-designed handle allows for better control and reduces hand fatigue during long cutting sessions.
Tip: Choose a hand saw with an ergonomic handle that fits comfortably in your palm — this improves accuracy and safety.
Blade
The blade is the flat, metal part of the saw that does the actual cutting. It’s made from high-carbon steel or stainless steel to ensure durability and sharpness. The length of the blade can vary depending on the type of hand saw and the material being cut.
Teeth
The teeth are the sharp, pointed edges along the bottom of the blade. They determine how fast and smooth the saw cuts. Fine-tooth saws create cleaner, slower cuts, while coarse-tooth saws are faster but rougher.
Example: A saw with 10 teeth per inch (TPI) cuts slower but smoother, while one with 6 TPI cuts faster but more roughly.
Heel
The heel is the part of the blade closest to the handle. It’s used to start the cut and offers better control for shorter or shallower cuts.
Toe
The toe is the opposite end of the blade the part farthest from the handle. It helps finish cuts and is often slightly narrower to reduce friction during sawing.
Back (or Spine)
Some hand saws, especially back saws, have a reinforced edge called the spine. This stiffens the blade, keeping it straight for precise cuts. However, it limits the depth of the cut since it prevents the blade from cutting too deep.
Teeth Set
The teeth set refers to the way the saw’s teeth are angled outward in alternating directions. This design creates a wider cut (kerf) than the blade itself, preventing it from getting stuck in the material.
Blade Tang (in certain saws)
In some hand saws, especially smaller models like coping saws, the tang connects the blade to the handle. It ensures a secure fit and steady movement while cutting.
Quick Summary
Each part of a hand saw from the handle to the teeth, works together to provide balance, control, and cutting efficiency. Knowing these components not only helps you choose the right saw but also ensures safer and more effective use.
Types of Hand Saws
When it comes to woodworking or DIY projects, understanding the different types of hand saws is essential. Each saw is designed for a specific purpose, and choosing the right one ensures clean, accurate, and efficient cuts. In this hand saw guide, we’ll explore the most common types and what makes each unique.
Crosscut Saw
A crosscut saw is designed to cut across the grain of the wood. It has sharp, beveled teeth that slice through fibers cleanly, making it ideal for cutting boards to length or trimming wood pieces. It’s a must-have for carpenters and general woodworkers.

Rip Saw
A rip saw is made for cutting along the grain. Its chisel-shaped teeth act like miniature planes, removing wood fibers in straight lines. This saw is perfect for ripping long boards and creating smooth, straight cuts.

Back Saw
A back saw features a reinforced spine along the top, giving it extra stability and precision. It’s commonly used with a miter box for fine woodworking and joinery. The tenon saw and dovetail saw are popular subtypes of back saws.

Coping Saw
A coping saw has a thin, narrow blade stretched across a U-shaped frame. It’s ideal for making curved or intricate cuts in wood, plastic, or even metal. Woodworkers often use it for decorative trim or coping joints in molding.

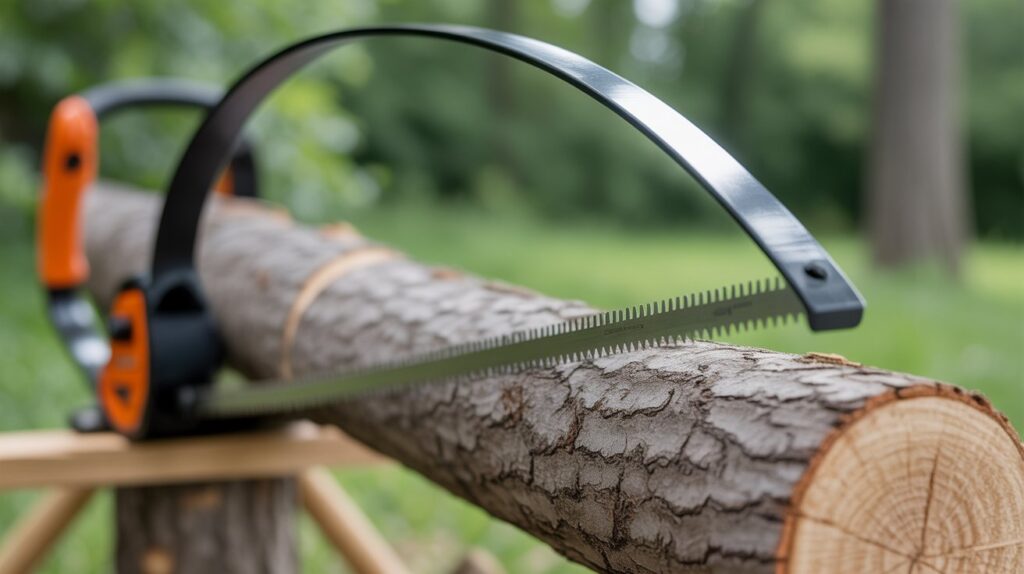
Bow Saw
A bow saw features a long, thin blade tensioned by a metal frame shaped like a bow. It’s designed for rough cutting and outdoor work, such as pruning trees or cutting logs. Its aggressive teeth make it great for fast, coarse cuts.

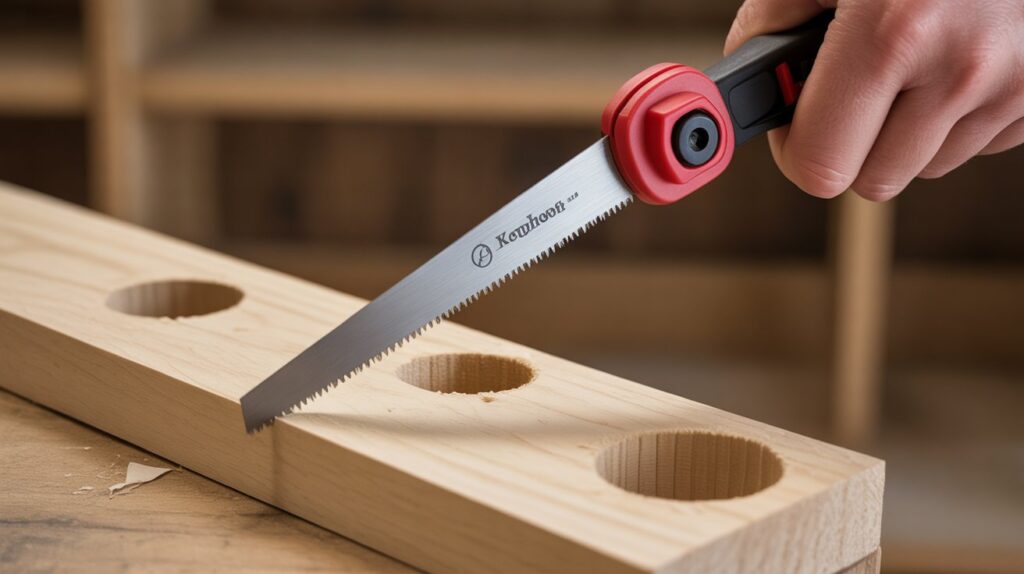
Keyhole (Compass) Saw
A keyhole (compass) saw has a long, narrow, pointed blade designed for cutting small holes and curved shapes in wood, drywall, or plastic. Its slim design allows it to reach tight spaces, making it ideal for detail work like cutting openings for pipes or electrical boxes.

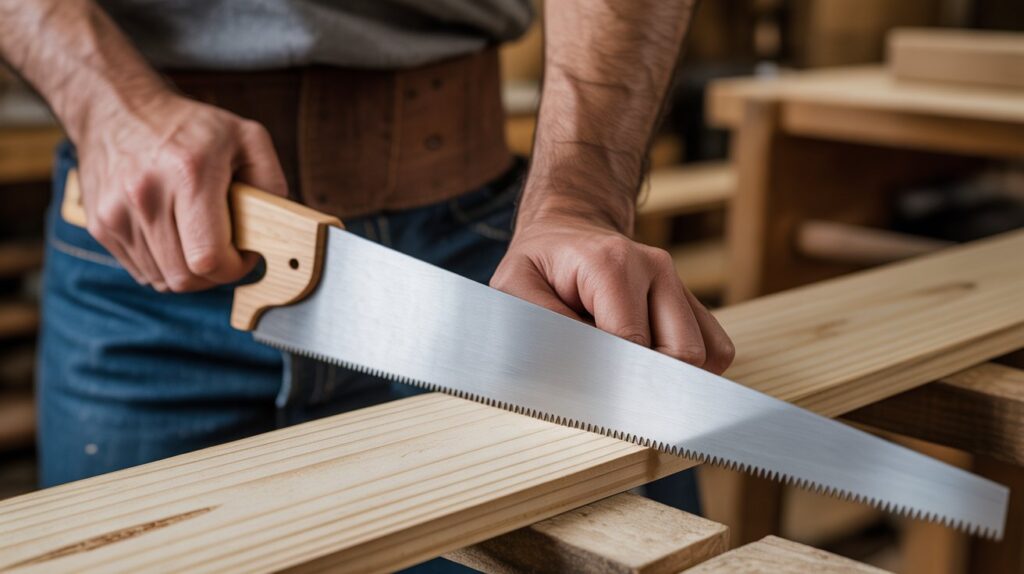
Japanese Saw (Ryoba or Dozuki)
A Japanese hand saw cuts on the pull stroke rather than the push stroke, offering more control and cleaner cuts. The Ryoba has teeth on both edges for crosscutting and ripping, while the Dozuki has a reinforced back for precision joinery.

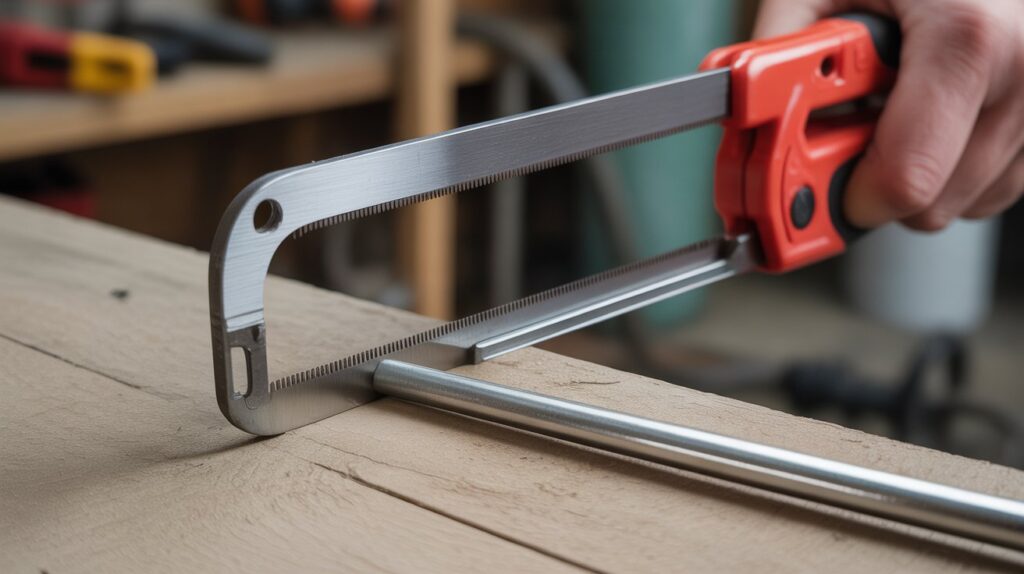
Hacksaw
A hacksaw is mainly used for cutting metal and plastic. It features a fine-toothed blade stretched across a C-shaped frame. It’s essential for plumbing, metalwork, and home repairs.

Quick Summary
Each type of hand saw serves a unique purpose. Whether you’re working on delicate joinery, rough lumber, or metal pipes, understanding which saw to use ensures better performance, cleaner cuts, and longer tool life.
Comparison Table: Best Hand Saws for Different Tasks
| Type of Hand Saw | Best For | Material Cut | Key Features | Skill Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crosscut Saw | Cutting wood across the grain | Wood | Sharp, beveled teeth for clean cuts | Beginner–Intermediate |
| Rip Saw | Cutting wood along the grain | Wood | Chisel-shaped teeth for smooth, straight cuts | Intermediate |
| Back Saw (Tenon/Dovetail) | Precision joinery and fine woodworking | Wood | Reinforced spine for accuracy | Intermediate–Advanced |
| Coping Saw | Curved or intricate shapes | Wood, plastic, metal | Thin blade with high maneuverability | Beginner–Intermediate |
| Bow Saw | Outdoor and rough cutting | Wood, logs | Sturdy metal frame, fast coarse cutting | Beginner |
| Keyhole (Compass) Saw | Cutting small openings or curves | Wood, drywall, plastic | Pointed blade for detailed interior cuts | Beginner–Intermediate |
| Japanese Saw (Ryoba/Dozuki) | Clean, precise joinery cuts | Wood | Pull-stroke design for fine control | Intermediate–Advanced |
| Hacksaw | Cutting metal and plastic pipes | Metal, PVC | Fine-toothed replaceable blade | Beginner–Intermediate |
Quick Buying Tip
When choosing the right hand saw, think about:
- Material — Wood, metal, or plastic?
- Type of cut — Straight, curved, or fine joinery?
- Frequency of use — Occasional DIY or daily professional use?
- Comfort and control — Choose a saw with an ergonomic handle and good balance.
How to Choose the Right Hand Saw
Choosing the right hand saw is an important step in getting clean, accurate, and efficient cuts. In this Hand Saw Guide, we’ll help you understand what to look for so you can pick the perfect saw for your job.
1. Consider the Material You’ll Cut
Different hand saws are designed for specific materials.
- Wood: Use a crosscut or rip saw depending on the grain direction.
- Metal: Choose a hacksaw with fine teeth.
- Plastic or PVC: A keyhole or coping saw works best for curved or small cuts.
2. Check the Teeth Per Inch (TPI)
The number of teeth per inch affects how smooth or fast your cut will be.
- Low TPI (7–10): Cuts faster but rougher, suitable for thick wood.
- High TPI (11–20): Cuts slower but gives a cleaner finish, ideal for fine woodworking.
3. Select the Right Blade Length
Longer blades make longer cuts and stay straighter, while shorter blades are easier to control for detailed work.
- For general woodwork, a 20–24 inch blade works well.
- For smaller tasks, choose a 10–14 inch blade.
4. Look at the Handle Design
A comfortable handle improves control and reduces hand fatigue. Test the grip—your hand should fit naturally, and the handle should feel balanced with the blade.
5. Match the Saw to Your Project Type
- For carpentry and large cuts: Crosscut or rip saw.
- For furniture or fine cuts: Back saw or dovetail saw.
- For curved or detailed cuts: Coping or keyhole saw.
6. Check Quality and Durability
Choose a saw made from high-carbon steel or stainless steel for longer life. Make sure the teeth are sharp and evenly spaced. A rust-resistant coating is also helpful.
7. Think About Budget and Brand
Good quality doesn’t always mean expensive. Look for trusted brands with good reviews, and compare features before buying.
By following these steps from our Hand Saw Guide, you can confidently choose the right tool for any project—ensuring better performance, accuracy, and safety.
Best Brands and Models of Hand Saws
When choosing a hand saw, the brand matters because it shows the quality, durability, and cutting performance. In this Hand Saw Guide, here are some of the best brands and models that professionals and DIY users trust:
1. Stanley – Known for its strong blades and comfortable grip. The Stanley FatMax Hand Saw is great for smooth and fast cutting in both soft and hard wood.
2. Irwin – Offers sharp, long-lasting blades. The Irwin Universal Hand Saw is a popular model because it cuts quickly and stays sharp for a long time.
3. Bahco – Famous for its precision and balance. The Bahco 2600-XT is ideal for fine and accurate cuts.
4. Spear & Jackson – A trusted name in hand tools. Their Predator Hand Saw line is well-balanced and perfect for general wood cutting.
5. Craftsman – Known for reliable tools at affordable prices. The Craftsman 20-Inch Hand Saw is durable and easy to control for beginners.
How to Use a Hand Saw Safely
Using a hand saw safely is very important for both beginners and professionals. In this Hand Saw Guide, follow these easy steps to work safely and get the best cutting results.
1. Wear Safety Gear
Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from wood dust and small pieces. Use gloves if needed for a better grip.
2. Secure the Material
Before cutting, fix the wood or metal piece firmly using a clamp or vise. This keeps it from moving and helps you cut accurately.
3. Hold the Saw Properly
Grip the handle firmly with one hand and keep your other hand away from the blade. Maintain a steady and comfortable posture.
4. Start Slowly
Begin cutting with light strokes to make a small groove. Once the saw is steady in the groove, increase your speed gradually.
5. Let the Saw Do the Work
Do not push too hard. Let the saw’s sharp teeth cut smoothly through the material. Forcing the saw can bend or damage the blade.
6. Keep the Work Area Clean
Always work on a clean, flat surface and remove sawdust regularly so you can see your cutting line clearly.
7. Store Safely After Use
After finishing your work, clean the blade and store the hand saw in a dry place to prevent rust.
Hand Saw Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance helps your hand saw last longer and perform better. In this Hand Saw Guide, here are some simple tips to keep your saw in good condition.
1. Clean After Every Use
After cutting, wipe the blade with a dry cloth to remove sawdust and dirt. For sticky residue, use a little oil or mild cleaner.
2. Keep the Blade Oiled
Apply a thin coat of light machine oil on the blade to prevent rust. This also keeps the saw moving smoothly during cutting.
3. Sharpen the Teeth Regularly
A dull blade makes cutting harder and less accurate. Use a saw file or take it to a professional for sharpening when needed.
4. Check for Damage
Inspect the handle and blade for cracks, rust, or bent teeth. Fix small problems early to avoid bigger issues later.
5. Store Properly
Store your hand saw in a dry place. Hang it on a wall or keep it in a tool box with a blade cover to protect it from moisture and dust.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using a Hand Saw
Even with a good tool, simple mistakes can make cutting harder and unsafe. In this Hand Saw Guide, here are common errors to avoid when using a hand saw.
1. Using the Wrong Type of Saw
Each saw is made for a specific job. Using a wood saw on metal or plastic can damage the blade and give poor results. Always choose the right saw for your material.
2. Forcing the Saw
Pushing too hard can bend the blade or make uneven cuts. Let the saw’s teeth do the work and move it smoothly back and forth.
3. Not Securing the Material
Cutting a loose piece of wood is dangerous. Always use a clamp or vise to hold your material steady before you start cutting.
4. Ignoring the Cutting Angle
Holding the saw at the wrong angle can cause crooked cuts. Keep a steady angle and follow your cutting line carefully.
5. Skipping Safety Gear
Many people forget to wear safety glasses or gloves. Protecting your hands and eyes is important every time you use a hand saw.
Avoiding these mistakes will make your work safer, faster, and more accurate. Adding a photo that shows the correct cutting position can help explain this better.
Benefits of Using a Hand Saw
In this Hand Saw Guide, it’s important to understand why many people still prefer hand saws even with modern power tools available. Here are the main benefits of using a hand saw.
1. Easy to Use
A hand saw is simple and doesn’t require electricity or setup. Anyone can use it with a little practice.
2. Portable and Lightweight
Because it’s small and light, you can easily carry a hand saw anywhere—perfect for quick jobs and outdoor projects.
3. Cost-Effective
Hand saws are affordable and need very little maintenance compared to power saws.
4. Precise Control
You have full control over the cutting speed and direction, which helps make clean and accurate cuts.
5. Quiet Operation
Unlike power saws, hand saws don’t make loud noise, making them ideal for home or indoor use.
6. Safe for Beginners
With basic safety steps, a hand saw is much safer to learn and use than electric tools.
Using a hand saw gives both professionals and hobbyists flexibility, control, and reliability in their work.
Hand Saw Buying Guide Checklist
Before buying a new hand saw, it’s important to know what to look for. This Hand Saw Guide will help you choose the right tool for your needs.
1. Blade Length
Choose a blade length based on your work. Longer blades are better for larger cuts, while shorter ones offer more control for fine cutting.
2. Teeth Per Inch (TPI)
TPI decides how smooth or rough your cut will be. A higher TPI (10–14) gives smoother cuts, while a lower TPI (6–8) is faster but rougher.
3. Handle Comfort
Pick a saw with a strong, comfortable handle. It should fit well in your hand to reduce strain during long use.
4. Weight and Balance
A well-balanced hand saw is easier to control and cuts more accurately. Avoid saws that feel too heavy or uneven.
5. Material and Blade Quality
Look for high-carbon steel or stainless steel blades. These last longer and resist rust better.
6. Price and Warranty
Compare prices and check for a warranty. A good hand saw doesn’t need to be expensive but should come from a trusted brand.
By following this checklist, you can confidently pick the best hand saw for your woodworking or DIY projects.
Conclusion
Choosing the right hand saw and using it properly can make any cutting job easier, safer, and more accurate. This Hand Saw Guide has covered everything you need to know — from the best brands and maintenance tips to safety advice and buying checklists.
A good hand saw is not just a tool; it’s an investment that helps you work smarter and achieve cleaner results. Whether you’re a beginner or a professional, understanding how to care for and use your saw correctly will extend its life and improve your work quality.
For more helpful guides and the best hand saws at great prices, visit CutterZone.com — your trusted source for quality cutting tools.
FAQs About Hand Saws
What is the best hand saw for beginners?
For beginners, a general-purpose crosscut hand saw is the best choice. It’s easy to handle, affordable, and works well for most wood-cutting tasks. Brands like Stanley or Irwin offer reliable options for first-time users.
How often should I sharpen my saw?
It depends on how often you use it. If you use your hand saw regularly, sharpen it every few months. For light or occasional use, sharpening once or twice a year is enough. Always sharpen when you notice rough or uneven cuts.
Can hand saws cut metal?
Yes, but only if you use the right type of hand saw. A hacksaw is designed for cutting metal. Standard wood saws should not be used on metal because they can damage the teeth and blade.
How do I prevent my hand saw from rusting?
To prevent rust, always clean your saw after use and wipe the blade with a light coat of oil. Store it in a dry place or inside a toolbox with a blade cover to protect it from moisture.
Can I use a hand saw for plastic or PVC?
Yes, you can. A fine-tooth hand saw or a hacksaw works well for cutting plastic or PVC pipes. Just make sure to cut slowly and evenly to avoid cracking the material.
